Australian Water Tank Regulations: State-by-State Guide
Jump to section
- Overview
- Understanding National Water Tank Standards
- Key National Requirements for Rainwater Tanks
- NSW Water Tank Regulations
- Victoria’s Water Tank Requirements
- South Australia’s Rainwater Tank Regulations
- Queensland Water Tank Regulations
- Water Tank Requirements in Canberra
- Choosing the Right Water Tank for Your Property
- Water Tank Sizing Calculator
- Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
- Ensuring Compliance and Efficiency
When considering the purchase of rainwater tanks for your property, it’s essential to ask a few key questions to ensure you make the right choice. One of the most common questions is, “What size water tank do I need?” The answer depends on several factors, including your household’s water usage, roof area, and local climate. It’s important to calculate the appropriate size, as choosing the wrong tank can affect your water supply efficiency and may not meet your needs during dry periods.
Another critical consideration is understanding the council regulations for water tanks in your area. Depending on where you live, there may be specific rainwater tank installation regulations you need to comply with, such as obtaining permits or meeting certain installation standards. You might be wondering, “Do I need council approval for a water tank?” or “Do you need a permit for a water tank?” These are crucial questions, as failing to adhere to local water tank building regulations could result in fines or the need to modify your installation.
For those living in bushfire-prone areas, bushfire water tank requirements and CFA water tank requirements (or CFS water tank requirements in South Australia) are particularly important. These regulations ensure that your residential water tank is equipped to provide adequate water for firefighting efforts in the event of an emergency. Additionally, fire fighting water tank requirements often specify the minimum tank capacity and connection points that must be included in your installation to comply with safety standards.
When it comes to rainwater storage tanks for drinking purposes, questions like “Does tank water need to be filtered?” and “What are the potable water storage tank regulations?” are common. Ensuring that your drinking water storage tanks are properly maintained and filtered is crucial for health and safety. Water tank inspection requirements and water tank testing requirements are also essential to guarantee that your water remains clean and safe for consumption.
For those building a new home, understanding new home water tank regulations and water storage tank requirements is vital. Whether you’re installing a rainwater collection tank for household use or a town water tank for additional storage, being aware of the requirements of water tank in residential building codes in Australia is key to ensuring your installation is compliant and effective. Additionally, considering the roof area required for a water tank can help determine the most efficient setup for your property.
By addressing these questions and understanding the relevant water tank requirements, you can ensure that your rainwater tank installation meets both your needs and regulatory standards.
Given the critical importance of water conservation, state governments across Australia have implemented specific regulations for rainwater tanks. However, these requirements vary from state to state. This guide aims to navigate you through the water tank regulations in New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and the Australian Capital Territory, ensuring compliance and effective water management.
Understanding National Water Tank Standards
The National Construction Code (NCC) is the cornerstone of Australia’s building and plumbing standards, ensuring that construction meets the essential requirements for safety, health, accessibility, and sustainability. Produced and maintained by the Australian Building Codes Board on behalf of the government, the NCC establishes a uniform standard across the nation, setting the minimum performance levels that buildings must achieve. This consistency is crucial for maintaining the quality of construction and plumbing work, including the installation and maintenance of water tanks.
One of the key elements of the NCC is the “6 Star Standard” for energy efficiency and water conservation, which forms part of the Nationwide House Energy Rating Scheme (NatHERS). This standard aims to optimise a home’s energy use by assessing factors like design, materials, and construction methods. The star rating system, ranging from 0 to 10, evaluates how efficiently a home can maintain a comfortable temperature throughout the year. Recent updates to the NCC have introduced a new minimum 7-star rating, along with an annual energy use budget for the entire home, including fixed appliances, solar panels, and batteries. This ensures that homes are designed not just for comfort but also for energy efficiency and sustainability.
In addition to the NCC, compliance with the AS/NZS 3500 standards is essential for all plumbing and drainage work related to water tanks. This set of standards, known as the National Plumbing and Drainage Code, outlines the requirements for materials, design, and installation of various services, including stormwater drainage, which is particularly relevant for water tanks. The AS/NZS 3500 standards apply to new installations as well as alterations, additions, and repairs to existing systems, ensuring that all plumbing work meets the high standards necessary for effective water management and conservation. To learn more about the plumbing and drainage code, you can view section three on the NCC website.
AS/NZS 4766:2006 is a crucial Australian and New Zealand standard that focuses on the design and manufacture of polyethylene water tanks. This standard ensures that polyethylene tanks are engineered and produced to be fit for purpose, providing reliable storage for water and chemicals under normal conditions. Certification to AS/NZS 4766 is a mark of quality, indicating that a third party has verified the manufacturer’s compliance with all aspects of the standard. While not all manufacturers opt for certification, purchasing tanks from those who do gives you the highest level of confidence in their durability and safety.
Bushmans facilities are certified AS/NZS 4766:2006 and all of our tanks are made to the highest quality. If you would to like learn more you can read AS/NZS 4766:2006 documentation.
Key National Requirements for Rainwater Tanks
When installing rainwater tanks across Australia, it’s essential to adhere to key national requirements to ensure optimal performance, safety, and compliance with council regulations for water tanks. One of the first considerations is the minimum roof catchment area. Research indicates that better yield outcomes are achieved by maximising the roof area directed to the rainwater harvesting system. The minimum roof area required is typically the greater of 100 square metres or 50% of the roof area. A properly installed guttering system will connect approximately 100 square metres of roof catchment to the rainwater tank via two downpipes, though larger areas may require additional downpipes or a charged connection to the tank.
Protecting your rainwater storage tanks from mosquitoes and pests is another critical requirement. To achieve this, it’s essential to install an inlet strainer with a mesh size of less than 1mm, typically made from 316 stainless steel. This fine mesh prevents mosquitoes and other vermin from entering the tank while minimising debris ingress. Additionally, positioning the rainwater pump on the opposite side of the tank from the inlet can help maintain water quality by reducing sediment build-up. For enhanced protection against algae growth, consider using a light guard or solar shield, though a well-designed rainwater collection tank system should suffice in preventing sediment and nutrient accumulation.
Proper stormwater drainage is vital to the long-term integrity of your property. An effective stormwater drainage system redirects water efficiently, safeguarding the exterior walls, roof, and foundations from water damage. This is particularly important in preventing soil erosion, which can compromise the stability of your home. By directing overflow water from your residential water tank to appropriate areas such as gardens or designated ground areas, you not only minimise the impact on municipal stormwater systems but also improve soil quality and reduce environmental impact. Always ensure that rainwater overflow does not adversely affect neighbouring properties and complies with local water tank building regulations.
Adhering to these national requirements for installing water tanks, including those specific to rainwater tank installation regulations, ensures that your system is both compliant and efficient. Whether you’re considering a potable water storage tank, a town water tank, or addressing fire fighting water tank requirements, following these guidelines will help you choose the right system and maintain it effectively. For properties in bushfire-prone areas, additional considerations such as CFA or CFS water tank requirements may apply, so always check with local authorities for specific council requirements for water tanks in your area.
NSW Water Tank Regulations
When planning to install water tanks in NSW, understanding the regulations and requirements is crucial to ensuring compliance and maximising efficiency. The state of New South Wales has specific guidelines, particularly for new residential developments, under the Building Sustainability Index (BASIX). BASIX is a sustainability assessment tool designed to reduce the environmental impact of new homes by mandating standards for water and energy efficiency, as well as thermal performance.
One of the key objectives of BASIX is to achieve a 40% reduction in potable water usage compared to pre-BASIX benchmarks. This goal is particularly relevant in coastal regions of NSW, where most new residential developments are subject to this target. The BASIX water targets vary by location, taking into account the local climate, rainfall patterns, and current water usage. In many areas, rainwater tanks play a critical role in meeting these targets by providing a sustainable source of water for household use, including toilets, washing machines, and irrigation systems.
For those installing water tanks in NSW, it’s important to ensure the tank’s capacity and roof catchment area meet the BASIX assessment criteria. Typically, the larger the roof area connected to the tank, the more effective the rainwater harvesting system will be. In addition, proper management of overflow water is essential to prevent any adverse impact on neighbouring properties and to comply with local stormwater regulations. For further reading on NSW water tank regulations and BASIX, see the BASIX Water Review –Stage 1.
While BASIX provides a framework for sustainability, local councils in NSW may have additional requirements. For example, water tanks in Sydney and other parts of NSW that can store up to 10,000 liters of water typically do not require council approval, provided certain conditions are met. However, it’s essential to check with your local council and refer to the latest NSW Housing Code for any specific regulations that may apply. See Sydney Water’s information page for the further information about water tank regulations in Sydney.
When installing rainwater tanks in NSW, especially in new homes, it’s crucial to follow these guidelines to not only comply with water tank regulations in NSW but also to contribute to the state’s water conservation efforts. For those using rainwater for internal purposes, such as in toilets or washing machines, additional considerations like backflow prevention devices and proper plumbing connections are necessary. Always ensure that the tank is installed on a stable foundation and is not positioned over water or wastewater mains, as tanks become extremely heavy when full.
By adhering to these rainwater tank requirements in NSW, you can optimise the use of water tanks in New South Wales and support the state’s commitment to sustainability and water conservation. Whether you are installing water tanks in NSW Australia or specifically water tanks in Sydney, understanding these regulations will help you make informed decisions and ensure compliance.
Victoria’s Water Tank Requirements
In Victoria, the installation and use of rainwater tanks are governed by specific regulations designed to ensure both safety and compliance with local council standards. These regulations play a crucial role in supporting water storage in Victoria and contribute to the state’s sustainability efforts. Whether you’re installing water tanks in Victoria, Australia for a new home or upgrading an existing system, understanding these requirements is essential.
For new residential developments (class 1 buildings), water tank requirements in Victoria stipulate that a rainwater tank must have a minimum capacity of 2,000 litres, connected to a roof catchment area of at least 50 square metres. This tank should also be linked to all toilets in the home for sanitary flushing purposes. This regulation is part of the broader 6-star building requirements, which are designed to enhance water efficiency and reduce reliance on mains water.
When it comes to the service installation rules in Victoria, any plumbing work associated with the installation of a water tank must be performed by a licensed or registered plumber. This includes connecting the roof catchment to the tank, as well as the tank overflow to the stormwater drain. Plumbing jobs valued at $750 or more, including the tank, fittings, and labour, require the plumber to issue a compliance certificate, ensuring that all work meets the relevant Australian standards and guidelines, such as AS/NZS 3500 for plumbing and drainage. See the Victorian Building Authority’s Rainwater Tank Installation Checklist for a comprehensive checklist for installing a rainwater tank in Victoria, Australia.
It’s also important to note that while a building permit is not required for a free-standing water tank located externally, a permit may be necessary if the tank is installed within a building due to the structural implications of its weight when full. Ensuring that the rainwater tank is properly supported on a firm base, as per the manufacturer’s instructions, is critical to prevent any potential hazards.
Additionally, water tank regulations in Victoria include specific requirements to prevent backflow and cross-contamination, ensuring that the water stored in the tank remains safe for its intended use. Overflows must be properly managed to prevent structural damage, flooding, or instability of the tank itself.
For those considering water storage in Victoria, especially for new homes, adhering to these regulations and installation standards is essential to ensuring a safe and efficient system. Compliance not only supports Victoria’s water storage goals but also ensures that your installation meets all necessary water tank requirements for new homes in Victoria, contributing to a sustainable and secure water supply for your property. Bushmans strongly advises consulting your local council in Victoria to ensure compliance with any specific regulations that may apply.
South Australia’s Rainwater Tank Regulations
In South Australia, rainwater tanks are an essential component of new residential builds, reflecting the state’s commitment to water conservation. Specific regulations govern the installation and use of these rainwater tanks, with requirements varying across different councils, particularly in Adelaide and broader South Australia. Understanding these regulations is crucial for homeowners and builders to ensure compliance and to maximise the benefits of rainwater harvesting.
One of the key requirements for new homes in South Australia is the mandatory installation of a rainwater tank. The minimum size of the tank varies from council to council, but generally, the storage capacity must not be less than one kilolitre or 1000 litres. This requirement is in addition to any other water storage tanks that may be necessary, such as those used for bushfire protection. It is important to contact your local council to understand the specific requirements in your area, as these can influence the choice of tank size, type, and placement.
In Adelaide and across South Australia, the building rules stipulate that rainwater tanks must be plumbed to essential household fixtures, such as toilets, water heaters, or all cold water outlets in the laundry. Since 2006, new builds or significant extensions (over 50 square metres) that include these household fixtures, this connection to a water tank is mandatory. The installation must be carried out by a licensed plumber, ensuring that the system is compliant with AS/NZS 3500 and the South Australian variations. The plumbing system must include features like an overflow device and a mosquito-proof screen to maintain water quality and safety.
For rainwater systems that are interconnected with mains water, additional precautions are required. This includes installing backflow prevention devices, such as a dual check valve, to protect the mains water supply from contamination by the rainwater system. The rainwater supply system must also be clearly labelled, with all pipes and outlets identified as “RAINWATER” to prevent any confusion with potable water supplies.
Maintenance and safety are also emphasised in South Australia’s regulations. While domestic rainwater tanks do not require regular chemical or microbiological testing, it is recommended to perform routine checks to ensure the tank and plumbing system remain in good condition. For commercial or community-based tanks, however, regular water quality testing is mandatory to ensure the water is safe for drinking. Additionally, the tank must be securely installed on a firm base, as a filled tank can weigh several tonnes, posing a risk if not properly supported.
In summary, South Australia’s rainwater tank regulations are designed to ensure that all new builds are equipped with a reliable and safe water supply system, tailored to the specific needs of the area. By following these guidelines and consulting with local councils, homeowners can ensure they meet all water tank regulations in South Australia, contributing to the state’s broader water conservation goals. Whether you’re installing a rainwater tank in Adelaide, South Australia or elsewhere in SA, adhering to these rules will help you make the most of your water storage system. For more information on rainwater tank requirements in SA, read SA Water’s Rainwater Plumbing Guide.
Queensland Water Tank Regulations
In Queensland, the installation of rainwater tanks can be either voluntary or mandatory, depending on the location and the type of building. These requirements are governed by the Queensland Development Code (QDC) and local council regulations, which set out specific standards to ensure the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of rainwater systems.
For new residential buildings in approved local government areas that have opted into the QDC, the installation of a rainwater tank is often mandatory. These tanks must meet certain criteria, including a minimum capacity of 5,000 litres for detached houses and 3,000 litres for non-detached dwellings such as townhouses and terrace houses. Additionally, the rainwater tank must be connected to at least half of the available roof catchment area or 100 square metres, whichever is lesser.
The Queensland Development Code also stipulates that the rainwater tank must be connected to specific fixtures within the home. These include all toilet cisterns, cold water taps for washing machines, and at least one external tap, typically used for garden irrigation. To ensure a continuous water supply, especially during dry periods, the tank should be equipped with an automatic switching device or a trickle top-up system that integrates with the reticulated town water supply.
In terms of health and safety, Queensland’s Public Health Regulation 2018 mandates that all rainwater tanks must be mosquito-proof. This is achieved by installing screens with a mesh size of no more than 1mm at every tank opening, or by using flap valves that close automatically. These measures are crucial in preventing the breeding of mosquitoes and other vermin within the tank, thereby ensuring the safety of the water supply. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, so it’s important to adhere to these standards strictly.
The QDC also requires the installation of a first flush diverter when rainwater is used indoors or as stipulated by local government planning instruments. This device is essential for diverting the initial flow of water, which may carry debris and contaminants, away from the tank, ensuring that only clean water enters the storage system.
In addition to these state-wide requirements, local councils in Queensland may impose additional regulations or standards based on regional needs and environmental considerations. It’s advisable to consult with your local council to understand any specific requirements that may apply to your area, particularly regarding the installation of rainwater tanks and their connection to stormwater systems.
By following these water tank regulations in Queensland, homeowners can ensure that their rainwater tanks are compliant, efficient, and safe. Whether you’re voluntarily installing a rainwater tank or are required to do so under the QDC, adhering to these guidelines will help you make the most of your water storage system in Queensland, supporting both environmental sustainability and water security. For a comprehensive guide to rainwater tank regulations in QLD, you can read MP 4.2 – Rainwater Tanks And Other Supplementary Water Supply Systems.
Water Tank Requirements in Canberra
When installing water tanks in Canberra, it’s essential to follow the specific guidelines and regulations set by the ACT Government to ensure compliance and support water conservation efforts. Whether you are building a new home, redeveloping, or making significant extensions to an existing property, adhering to these ACT water tank requirements is crucial.
In the Australian Capital Territory, water tank installations must align with the principles of Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD). These principles aim to reduce the demand for potable water by utilising alternative sources such as rainwater, minimise wastewater, and enhance the quality of stormwater before it is discharged into waterways. Canberra water tanks play a key role in achieving these goals, helping to reduce the strain on the city’s water supply and improve the health of local catchments and waterways.
For all residential developments, the ACT Government’s “Think water, act water” strategy encourages the use of rainwater tanks to reduce mains water consumption. By 2023, the strategy aims to reduce Canberra’s per capita mains water consumption by 25%. Installing a water tank in Canberra not only helps achieve these targets but also provides homeowners with a way to save on their water bills and reduce their environmental impact.
Canberra water tank installation comes with specific requirements. For instance, tanks must be installed on a strong, stable base capable of supporting the weight of a full tank—each kilolitre of water weighs one tonne. To prevent corrosion and ensure the longevity of the tank, it should be kept above ground on a self-draining base, and covers and lids must be impervious to prevent the entry of dust, leaves, insects, and other contaminants. For underground installations, it is crucial to seal the tank against surface runoff and groundwater to avoid contamination.
All water tank installations in Canberra require the use of a licensed plumber for connecting the tank to household plumbing systems, such as those supplying water to toilets, washing machines, and irrigation systems. The installation must include a mosquito-proof screen or flap valves at every opening to comply with health regulations and prevent mosquito breeding. Additionally, first flush diverters are recommended to ensure that the initial, potentially contaminated, runoff does not enter the tank.
Overflow management is another critical aspect of Canberra water tank installation. While it is common to connect the overflow to the household stormwater drainage system, it is also permissible to allow rainwater to flow directly into your yard, provided it does not cross property boundaries or cause flooding under buildings. Proper management of overflow is essential to prevent issues such as foundation damage, timber rot, and increased humidity under floors.
By adhering to these ACT water tank requirements, homeowners can ensure that their Canberra water tanks are installed safely, effectively, and in compliance with local regulations. These measures not only contribute to the sustainability of the region’s water resources but also help protect the health and functionality of Canberra’s urban environment. For the full guidelines for water tank installation in Canberra, check out the ACT Rainwater tanks: Guidelines for residential properties in Canberra.
Choosing the Right Water Tank for Your Property
Selecting the right water tank for your property involves careful consideration of several factors, including the intended use, roof area, water usage, and local rainfall patterns. Understanding these elements will help you determine the appropriate size and type of rainwater tank to meet your needs effectively.
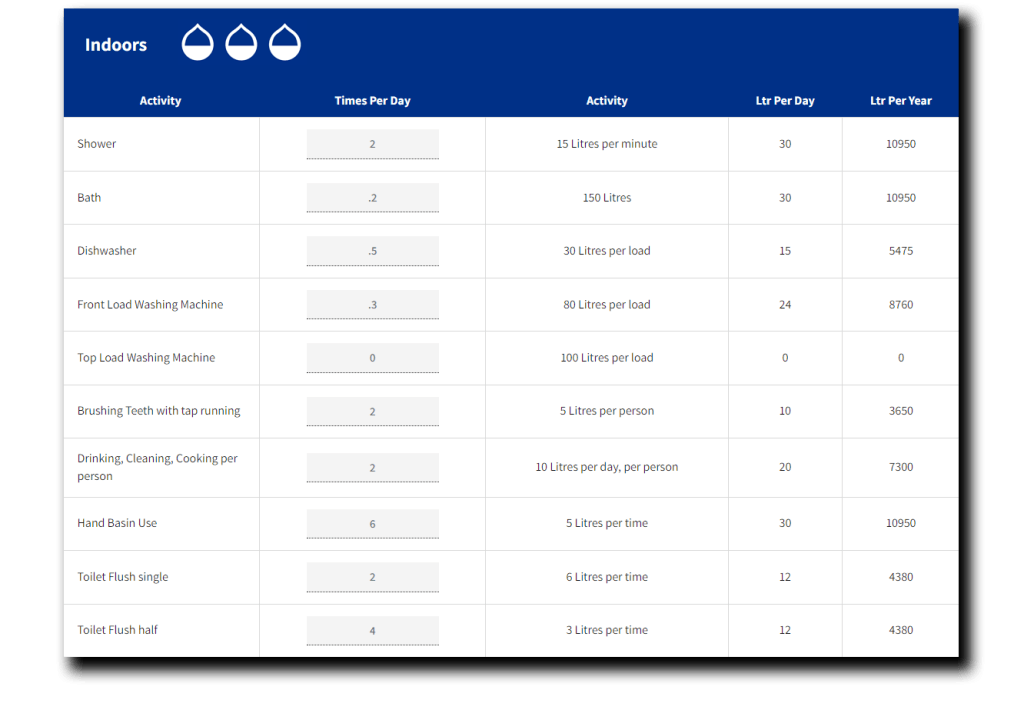
The first step in choosing the right water tank is to identify its purpose. Are you planning to use the tank solely for watering your garden, or do you need it to supply water to your entire household? For smaller applications like garden irrigation, where a mains water supply is available, the size of the tank may be less critical. However, if the tank is intended to supply water to your home, particularly for high-demand uses like toilet flushing or laundry, it’s important to calculate your household’s weekly water consumption. For example, each toilet flush uses approximately 9-11 litres of water, while running a washing machine consumes about 50 litres for a front loader and 120 litres for a top loader. By estimating the number of flushes and loads per week, you can get a better idea of the tank capacity you’ll need.
Another major consideration is your roof size and catchment area. The amount of rainwater you can harvest directly correlates with the area of your roof that is connected to the tank. Typically, the minimum roof area that should be connected to a rainwater tank is either 100 square metres or 50% of your roof area, whichever is greater. It is considered the correct way to install a gutter system on a standard roof to connect around 100 square metres of roof catchment to the tank, which is connected to the water tank via two downpipes. If your roof catchment area is larger, you may need to consider additional downpipes to maximise water collection.
Local rainfall patterns also play a crucial role in determining the right water tank size. In areas with low average rainfall, the amount of water you can harvest will be limited, making it necessary to choose a larger tank to ensure an adequate supply during dry periods. To assist with this, Bushmans provides a rainfall chart for Australia, allowing you to assess the typical rainfall in your region and plan accordingly.
Data sourced from Australian Bureau of Meteorology, among other sources, which can be viewed in table format here.
If your property does not have access to mains water and you rely entirely on a rainwater tank, it’s advisable to use a rainwater tank calculator to determine the ideal tank size. For large volumes of water storage, large round poly water tanks are a practical solution. Bushmans offers a range of these tanks, with capacities ranging from 10,000L to 46,400L. Multiple tanks can also be linked together to increase storage capacity. For even larger water storage needs, Aqualine steel water tanks are an excellent option, available in sizes from 20,000L to 360,000L. These tanks are built onsite and can be installed in areas with limited access.
When choosing between different tank materials, it’s important to consider both the pros and cons. Poly rainwater tanks are cost-effective, robust, and resistant to rust. Bushmans poly tanks are made with Sunsmart® technology, incorporating UV-stabilised materials that enhance the tank’s longevity in harsh Australian weather. However, poly tanks are manufactured in one piece, which can make them difficult to position on properties with limited access, which can require a crane for installation.
On the other hand, steel water tanks are incredibly durable and can be constructed in larger sizes. Since they are assembled onsite, steel tanks can be installed in hard-to-reach areas, including indoors. The downside is that steel tanks are prone to rust, particularly with constant exposure to moisture. Bushmans Aqualine steel tanks are galvanised, reducing the risk of corrosion, and do not require the regular replacement of sacrificial anodes, unlike some other steel tank options. Additionally, steel tanks tend to be more expensive due to the cost of materials and the labour involved in their assembly.
For urban or residential properties where space is at a premium, slimline water tanks or small round poly tanks are ideal. Slimline rainwater tanks are designed to fit neatly down the side of a house, offering efficient water storage without taking up too much space. Small round poly tanks are also a good option for residential backyards, providing sufficient capacity for garden watering and household use without overwhelming the available space.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the water tank that best suits your property’s needs, ensuring efficient and reliable water storage for years to come.
Water Tank Sizing Calculator
Determining the right size for your water tank is crucial to ensuring you have an adequate water supply to meet your needs. If you find yourself asking, “What size water tank do I need?”, Bushmans offers a helpful water tank sizing calculator that guides you through the process. This calculator considers key factors such as your roof size, household water usage, and the average annual rainfall in your area, making it easy to identify the correct tank size for your specific situation.
You can access the Bushmans water tank calculator here. Simply input your details, and the calculator will provide you with a recommended tank size that suits your needs. Additionally, Bushmans has put together a comprehensive blog, “What Size Water Tank Do I Need?” that covers a wide range of information regarding selecting the right tank size.
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, a simple formula can also help determine the appropriate water tank size: multiply your average daily water usage by the number of days between rainfalls.
For example, if your household uses 1,000 litres of water per day and the average time between significant rainfalls is 30 days, you would need a tank with a capacity of at least 30,000 litres. This formula provides a straightforward way to estimate your water storage needs based on your specific consumption and local weather patterns.
By using either the online water tank calculator or this manual formula, you can confidently choose a water tank that meets your requirements, ensuring a reliable and efficient water storage solution for your property.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your rainwater tank system. At Bushmans, we take pride in offering a full-service approach to the delivery and fitting of your water tank, making the process as seamless and stress-free as possible. Here’s an overview of the key steps involved in the installation process and the best practices for maintaining your water tank.
Installation Process
- Site Preparation: Before ordering your water tank, it’s important to assess your property for a suitable location. Consider the available space and roof area that can be plumbed to the tank. The site should be level and stable, with adequate access for delivery and installation. Check if there are any local council regulations concerning the placement of the tank near property boundaries or neighbouring fences.
- Preparing the Base: A solid base is essential to support the weight of the tank, especially when full. Most tanks, whether poly or steel, require a firm, level pad made of compacted sand, gravel, or concrete. This base will ensure the tank remains stable and secure over time. We have prepared a video, How To Prepare Your Base And Site for A Water Tank that is a helpful guide for preparing a base.
- Ordering and Delivery: Once you’ve prepared the site, you can order your water tank. When your tank is delivered, Bushmans skilled customer care delivery drivers will safely transport it to your property. Upon arrival, the tank is safely unloaded and, with assistance, rolled to its prepared base. The tank is then tipped and slid into its final position, ensuring it is perfectly aligned and secure.
- Installing Standard Fittings: After positioning the tank, our customer care team installs essential components, such as the overflow, ball valve, and outlet, according to your specifications. This step is crucial for ensuring your tank is ready for effective use.
- Professional Plumbing: While Bushmans assists with the placement and fitting of the tank, it’s essential to engage a licensed plumber to connect the tank to your home’s water system. This will ensure compliance with local regulations and AS/NZS 3500 standards, which govern plumbing and drainage systems in Australia. A professional plumber will properly integrate the tank with your property’s water system, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Maintenance Best Practices
Regular maintenance is vital to maintaining water quality and the efficiency of your rainwater tank system. Here are some key maintenance tasks to keep your tank in top condition:
- Roof and Gutter Cleaning: Regularly clear debris from your roof and gutters to prevent contaminants from entering the tank. Overhanging tree branches should be trimmed back to reduce the amount of organic matter that can accumulate in the gutters.
- Pre-Filtration System Maintenance: Clean the pre-filtration system, tank strainer, and first flush diverter every few months. The first flush diverter is particularly important as it helps reduce the amount of debris that enters the tank by diverting the initial flow of water away from the tank.
- Tank Cleaning: Periodically clean the bottom of the tank to prevent the build-up of sludge, which can affect water quality. If your tank hasn’t been cleaned regularly, it may be necessary to hire a professional rainwater tank cleaner to thoroughly clean and inspect the tank.
- Inspecting Fittings and Components: Regularly check the tank’s fittings, such as the overflow and ball valve, to ensure they are functioning correctly and are free of blockages. This helps maintain the system’s efficiency and prevents issues that could lead to water contamination or overflow problems.
By following these rainwater tank installation and maintenance best practices, you can ensure that your water tank operates efficiently, providing a reliable source of clean water for your property. Regular care and professional installation are key to maximising the lifespan and performance of your rainwater tank.
Ensuring Compliance and Efficiency
Understanding and complying with water tank requirements is essential for both the effectiveness of your water storage system and adherence to local regulations. Properly installed and maintained water tanks not only ensure a reliable water supply but also contribute significantly to sustainability and cost savings over time. Compliance with regulations, such as those outlined in the National Construction Code (NCC) and state-specific guidelines, is crucial to avoid potential fines and ensure the safety and functionality of your system.
Each region in Australia, Queensland, New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, Victoria and South Australia, has its own set of requirements, which may include specific tank capacities, roof catchment areas, and installation standards. For example, bushfire-prone areas might have additional requirements, such as CFA or CFS water tank specifications, to ensure adequate water supply during emergencies. Understanding these local nuances is vital, and consulting with your local council can help you navigate any specific regulations regarding tank placement, plumbing connections, and overflow management.
Engaging licensed professionals for the installation and maintenance of your water tank ensures that all work meets the necessary standards, such as those outlined in AS/NZS 3500 for plumbing and drainage. Additionally, Bushmans facilities comply with AS/NZS 4766: 2006, so you can be assured that every tank meets the highest standards of quality and durability.
By following these guidelines and working with experts, you can maximize the benefits of your water tank installation, supporting sustainable water use and reducing long-term costs through efficient water management.
Need further water tank advice? Fill out the contact form below